Description and operation. Diagnosis and testing
DESCRIPTION The rear suspension is comprised of (Fig. 1): CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber/
urethane bushings should be tightened with the
vehicle at normal ride height. It is important to have
the springs supporting the weight of the vehicle
when the fasteners are torqued. This will maintain
vehicle ride comfort and prevent premature bushing
wear. DESCRIPTION The top of the shock absorbers are bolted to the
body crossmember. The bottom of the shocks are
bolted to the axle brackets. OPERATION Ride control is accomplished through the use of
dual-action shock absorbers. The shocks dampen the
jounce and rebound as the vehicle travels over various
road conditions.
1 - STABILIZER LINK 2 - SHOCK 3 - LEAF SPRING 4 - STABILIZER BAR DESCRIPTION The stabilizer bar extends across the underside of
the vehicle and is bolted to the top of the axle. Links
at the end of the bar are bolted to the frame. OPERATION The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle body
roll. The spring steel bar helps to control the vehicle
body in relationship to the suspension. DESCRIPTION The rear suspension system uses multi-leaf single
stage springs and a solid drive axle. The forward end
of the springs are mounted to the body rail hangers
through rubber bushings. The rearward end of the
springs are attached to the body by the use of shackles.
The spring and shackles use rubber bushings.
The bushing help to isolate road noise. OPERATION The springs control ride quality and maintain vehicle
ride height. The shackles allow the springs to
change their length as the vehicle moves over various
road conditions. Spring and shock A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching components.
These noises can usually be stopped by tightening
the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attaching
components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermittent.
This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjustable.
If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The spring eye and shock absorber bushings do not
require any type of lubrication. Do not attempt to
stop spring bushing noise by lubricating them.
Grease and mineral oil-base lubricants will deteriorate
the bushing rubber.
If the vehicle is used for severe, off-road operation,
the springs should be examined periodically. Check
for broken and shifted leafs, loose and missing clips,
and broken center bolts. Refer to Spring and Shock
Absorber Diagnosis chart for additional information. SPRING AND SHOCK ABSORBER 2. Spring fatigue. 2. Replace spring. 2. Worn bushings. 3. Worn or missing spring tip inserts. 2. Replace bushings. 3. Replace spring tip inserts. 2. Worn bushings. 3. Leaking shock. 2. Replace shock. 3. Replace shock.Description and operation
Suspension component
Shock absorbers
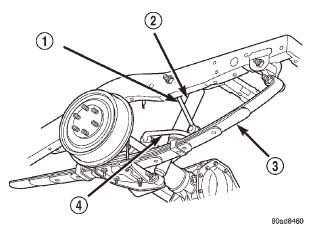 Fig. 1 Rear Suspension
Fig. 1 Rear SuspensionStabilizer bar
Leaf springs
Diagnosis and testing
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSES
CORRECTION
SPRING SAGS
1. Broken leaf
1. Replace spring.
SPRING NOISE
1. Loose spring clamp bolts.
1. Tighten to specification.
SHOCK NOISE
1. Loose mounting fastener.
1. Tighten to specification.
Dodge Durango (DN) 1998-2003 Service Manual
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and Driveline
- Brakes
- Cooling System
- Battery
- Starting Systems
- Charging System
- Ignition System
- Instrument Panel Systems
- Audio Systems
- Horn Systems
- Speed Control System
- Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems
- Wiper and Washer Systems
- Lamps
- Passive Restraint Systems
- Electrically Heated Systems
- Power Distribution System
- Power Lock Systems
- Vehicle Theft/Security Systems
- Power Seat System
- Power Window Systems
- Power Mirror Systems
- Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems
- Overhead Console Systems
- Engine
- Exhaust System
- Frame and Bumpers
- Fuel System
- Steering
- Transmission and Transfer Case
- Tires and Wheels
- Body
- Heating and Air Conditioning
- Emission Control Systems
- Introduction
