Electronic governor
DESCRIPTION
Governor pressure is controlled electronically. Components used for governor pressure control include:
- Governor body
- Valve body transfer plate
- Governor pressure solenoid valve
- Governor pressure sensor
- Fluid temperature thermistor
- Throttle position sensor (TPS)
- Transmission speed sensor
- Powertrain control module (PCM)
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid valve is a duty-cycle solenoid which regulates the governor pressure needed for upshifts and downshifts. It is an electro-hydraulic device located in the governor body on the valve body transfer plate (Fig. 63).
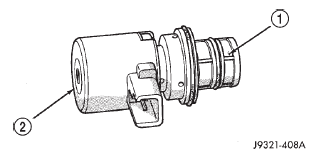 Fig. 63 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
Fig. 63 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
1 - SOLENOID FILTER
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
64).
 Fig. 64 Governor Pressure Sensor
Fig. 64 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmission line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower side of the transfer plate (Fig. 64).
TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
Transmission fluid temperature readings are supplied to the transmission control module by the thermistor.
The temperature readings are used to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure. Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room temperature is approximately 1000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission fluid at all times.
TRANSMISSION SPEED SENSOR
The speed sensor (Fig. 65) is located in the overdrive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the park gear and monitors transmission output shaft rotating speed.
 Fig. 65 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
Fig. 65 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance variations of two of the input devices. Though the slope of the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may vary due to various environmental factors or manufacturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the zero pressure offset is required to compensate for shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is below 200 RPM. A.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump), the governor pressure solenoid valve response may be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the.5 second calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued during this period, however the transducer output valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable reading. This value is retained and becomes the offset during the "cold" period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to produce governor pressure. The average current supplied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pressure.
Zero amps sets the maximum governor pressure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the trans control relay which supplies electrical power to the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts (DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the solenoid using the governor pressure solenoid control circuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to adequately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the solenoid valve through the governor body. It also channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that develops the necessary governor pressure.
TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature is below approximately 10C (50F).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126C (260F), the PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the converter clutch. Engagement is according to the third gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The overdrive OFF lamp in the instrument panel illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The transmission will not allow fourth gear operation until fluid temperature decreases to approximately 110C (230F).
TRANSMISSION SPEED SENSOR
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the transmission control module for processing. The vehicle speed sensor also serves as a backup for the transmission speed sensor. Signals from this sensor are shared with the powertrain control module.
Dodge Durango (DN) 1998-2003 Service Manual
- Lubrication and Maintenance
- Suspension
- Differential and Driveline
- Brakes
- Cooling System
- Battery
- Starting Systems
- Charging System
- Ignition System
- Instrument Panel Systems
- Audio Systems
- Horn Systems
- Speed Control System
- Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems
- Wiper and Washer Systems
- Lamps
- Passive Restraint Systems
- Electrically Heated Systems
- Power Distribution System
- Power Lock Systems
- Vehicle Theft/Security Systems
- Power Seat System
- Power Window Systems
- Power Mirror Systems
- Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems
- Overhead Console Systems
- Engine
- Exhaust System
- Frame and Bumpers
- Fuel System
- Steering
- Transmission and Transfer Case
- Tires and Wheels
- Body
- Heating and Air Conditioning
- Emission Control Systems
- Introduction
